| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
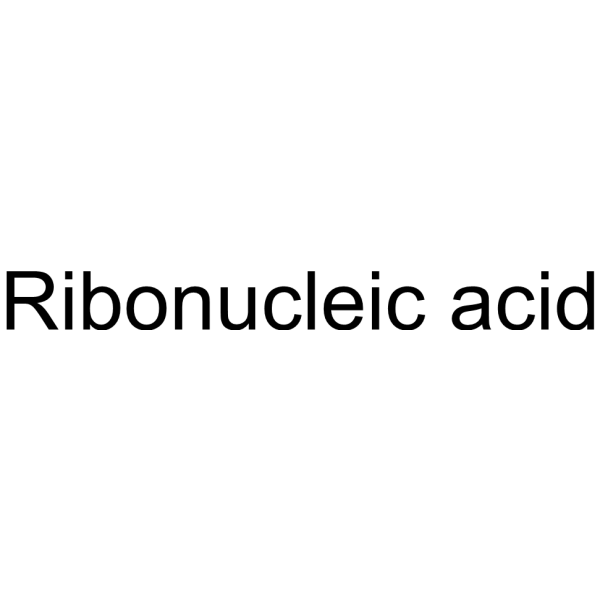 |
Ribonucleic acid
CAS:63231-63-0 |
|
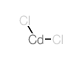 |
Cadmium chloride
CAS:10108-64-2 |
|
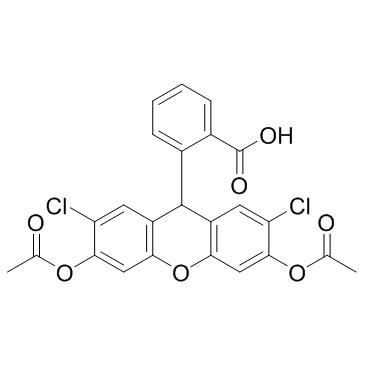 |
H2DCFDA
CAS:4091-99-0 |
|
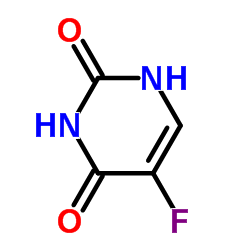 |
Aconitase from porcine heart
CAS:9024-25-3 |