| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Chloroform
CAS:67-66-3 |
|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
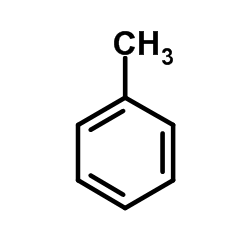 |
Toluene
CAS:108-88-3 |
|
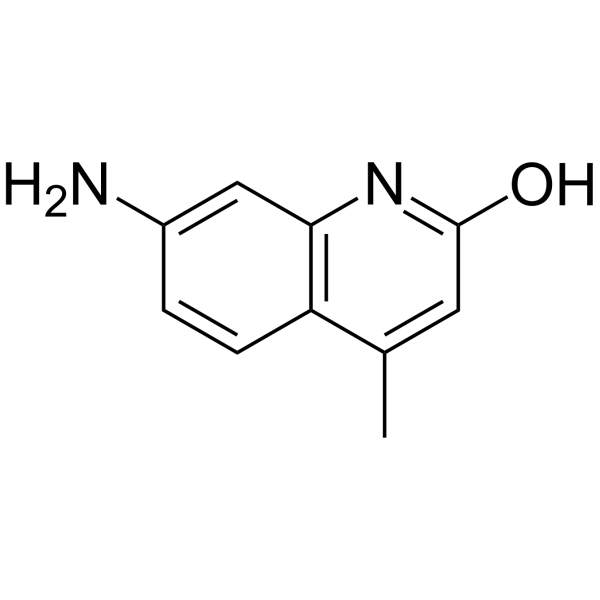 |
7-Amino-4-methylquinolin-2(1H)-one
CAS:19840-99-4 |