New monodisperse magnetic polymer microspheres biofunctionalized for enzyme catalysis and bioaffinity separations.
Daniel Horák, Jana Kučerová, Lucie Korecká, Barbora Jankovičová, Jiří Palarčík, Petr Mikulášek, Zuzana Bílková
Index: Macromol. Biosci. 12(5) , 647-55, (2012)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Magnetic macroporous PGMA and PHEMA microspheres containing carboxyl groups are synthesized by multi-step swelling and polymerization followed by precipitation of iron oxide inside the pores. The microspheres are characterized by SEM, IR spectroscopy, AAS, and zeta-potential measurements. Their functional groups enable bioactive ligands of various sizes and chemical structures to couple covalently. The applicability of these monodisperse magnetic microspheres in biospecific catalysis and bioaffinity separation is confirmed by coupling with the enzyme trypsin and huIgG. Trypsin-modified magnetic PGMA-COOH and PHEMA-COOH microspheres are investigated in terms of their enzyme activity, operational and storage stability. The presence of IgG molecules on microspheres is confirmed.Copyright © 2012 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
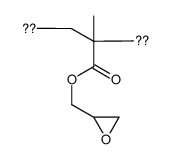 |
poly(glycidyl methacrylate) macromolecule
CAS:25067-05-4 |
C7H10O3 |
|
Adsorption and hydrolytic activity of trypsin on a carboxyla...
2012-09-01 [J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 381(1) , 125-36, (2012)] |
|
Reactive polymer as a versatile toolbox for construction of ...
2012-10-22 [Chemistry 18(43) , 13755-61, (2012)] |
|
Amine-functionalized polyglycidyl methacrylate microsphere a...
2013-03-25 [Macromol. Rapid Commun. 34(6) , 504-10, (2013)] |
|
Interactions of DPPC with semitelechelic poly(glycerol metha...
2012-11-06 [Langmuir 28(44) , 15651-62, (2012)] |
|
Condensation and polymerization of supersaturated monomer va...
2012-12-04 [Langmuir 28(48) , 16580-7, (2012)] |