| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Manganese chloride
CAS:7773-01-5 |
|
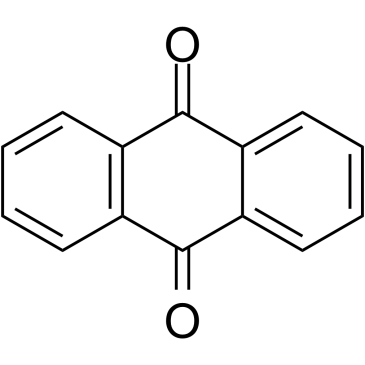 |
Anthraquinone
CAS:84-65-1 |
|
 |
Phosphine
CAS:7803-51-2 |
|
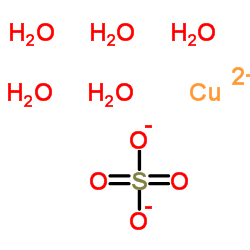 |
Cupric sulfate
CAS:7758-98-7 |
|
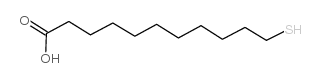 |
11-Mercaptoundecanoic acid
CAS:71310-21-9 |
|
 |
dichloroethane
CAS:107-06-2 |
|
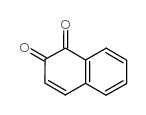 |
1,2-NAPHTHOQUINONE
CAS:524-42-5 |
|
 |
Magnesium choride
CAS:7786-30-3 |
|
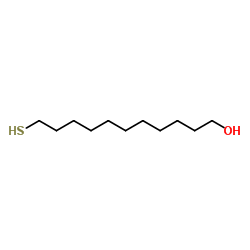 |
11-mercaptoundecanol
CAS:73768-94-2 |
|
 |
Phosphorus
CAS:7723-14-0 |