| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
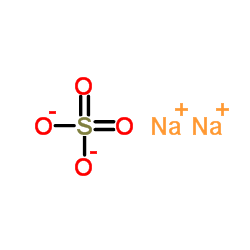 |
sodium sulfate
CAS:7757-82-6 |
|
 |
Cyclohexanone
CAS:108-94-1 |
|
 |
potassium chloride
CAS:7447-40-7 |
|
 |
Magnesium chloride hexahydrate
CAS:7791-18-6 |
|
 |
Calcium chloride
CAS:10043-52-4 |
|
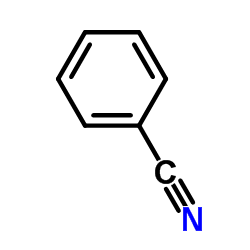 |
Benzonitrile
CAS:100-47-0 |
|
 |
acetic acid
CAS:64-19-7 |
|
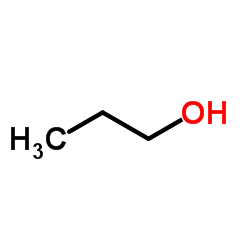 |
1-Propanol
CAS:71-23-8 |