| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
Acetone
CAS:67-64-1 |
|
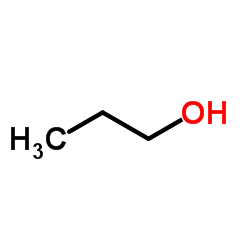 |
1-Propanol
CAS:71-23-8 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
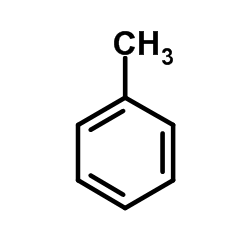 |
Toluene
CAS:108-88-3 |
|
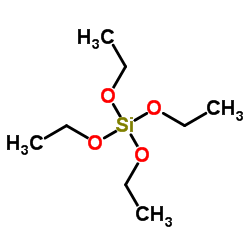 |
Tetraethyl orthosilicate
CAS:78-10-4 |
|
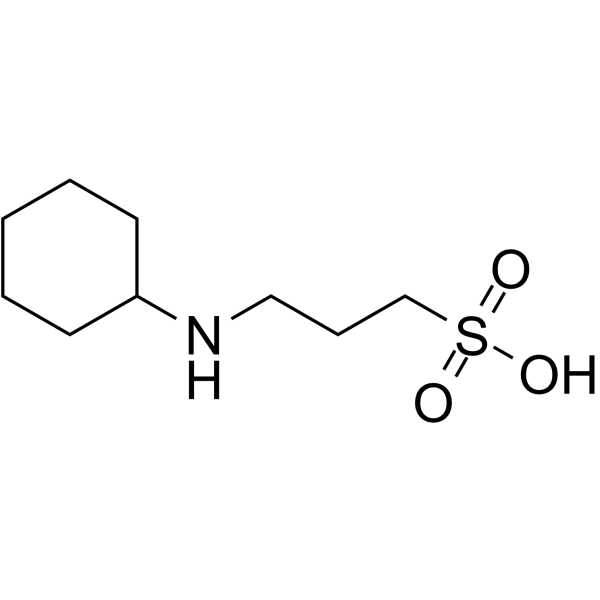 |
N-Cyclohexyl-3-aminopropanesulfonic acid
CAS:1135-40-6 |