| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
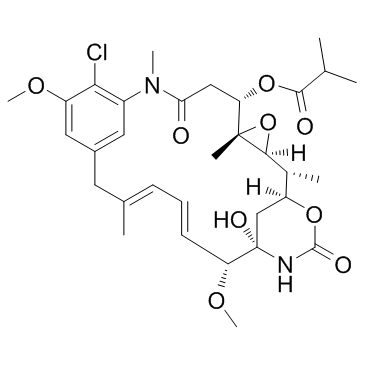 |
Ansamitocin P-3
CAS:66584-72-3 |
|
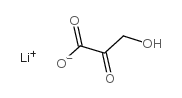 |
BETA-HYDROXYPYRUVIC ACID LITHIUM SALT HYDRATE
CAS:3369-79-7 |
|
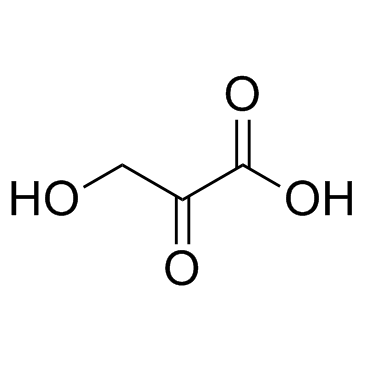 |
Hydroxypyruvic acid
CAS:1113-60-6 |