| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
styrene glycol
CAS:93-56-1 |
|
 |
(R)-1-Phenyl-1,2-ethanediol
CAS:16355-00-3 |
|
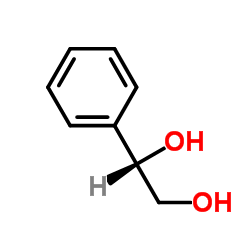 |
styrene glycol
CAS:25779-13-9 |