| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
N-hexane
CAS:110-54-3 |
|
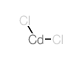 |
Cadmium chloride
CAS:10108-64-2 |
|
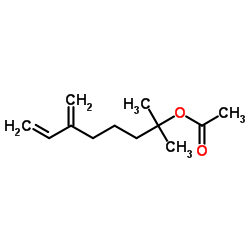 |
2-Acetoxy-2-methyl-6-methylene-7-octene
CAS:8006-64-2 |
|
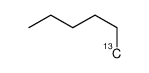 |
hexane
CAS:27581-27-7 |