Biodegradation of a synthetic lubricant by Micrococcus roseus.
M A Wright, F Taylor, S J Randles, D E Brown, I J Higgins
Index: Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59(4) , 1072-6, (1993)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
A bacterium that was able to utilize Emkarate 1550 (E1550), a synthetic lubricant ester, as the sole source of carbon was isolated. The isolate was tentatively identified as Micrococcus roseus. The components of the E1550 ester, octanoate, decanoate, and 1,1,1-tris(hydroxymethyl)propane (TMP), were detected in the culture medium of cells growing on the ester. The TMP tertiary alcohol accumulated during growth and was not utilized by this isolate. The detection of the components of the ester in the supernatant of cultures indicated that one of the first steps in its degradation was cleavage of the ester bonds. Esterase activity was significantly enhanced in cells grown on E1550 compared with esterase activity measured in cells grown on acetate.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
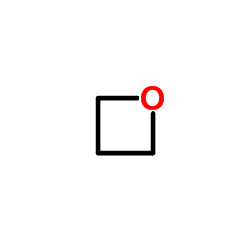 |
Trimethylol propane
CAS:77-99-6 |
C3H6O |
|
Preparation and mechanical properties of photo-crosslinked p...
2015-01-01 [Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 60 , 3-11, (2015)] |
|
Molecular Differentiated Initiator Reactivity in the Synthes...
2015-01-01 [Molecules 20 , 20131-45, (2015)] |
|
Investigation of thiol-ene and thiol-ene-methacrylate based ...
2010-01-01 [Dent. Mater. 26(1) , 21-8, (2010)] |
|
Modeling of reaction kinetics for transesterification of pal...
2010-01-01 [Bioresour. Technol. 101(15) , 5877-84, (2010)] |
|
Neurotoxin formation from pilot-scale incineration of synthe...
1996-01-01 [Arch. Toxicol. 70(8) , 508-9, (1996)] |