| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
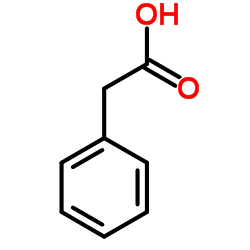 |
Phenylacetic acid
CAS:103-82-2 |
|
 |
Dimethyl sulfoxide
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
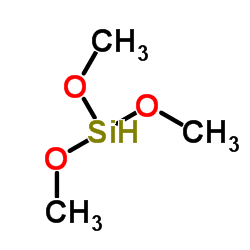 |
Trimethoxysilane
CAS:2487-90-3 |
|
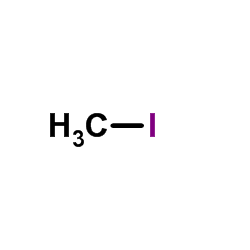 |
methyl iodide
CAS:74-88-4 |
|
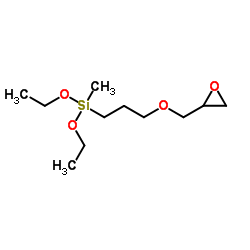 |
(3-Glycidoxypropyl)methyldiethoxysilane
CAS:2897-60-1 |
|
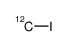 |
iodomethane
CAS:1173018-72-8 |
|
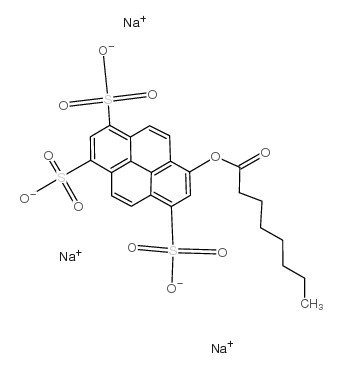 |
8-Octanoyloxypyrene-1,3,6-trisulfonic acid trisodium salt
CAS:115787-84-3 |
|
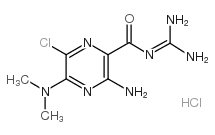 |
5-(N,N-Dimethyl)amiloride hydrochloride
CAS:1214-79-5 |