| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
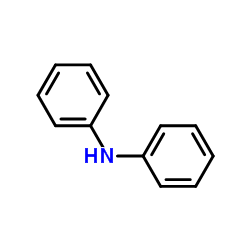 |
Diphenylamine
CAS:122-39-4 |
|
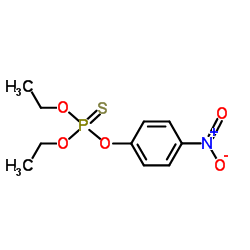 |
Parathion
CAS:56-38-2 |
|
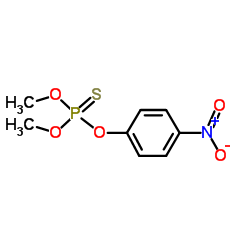 |
Parathion methyl
CAS:298-00-0 |
|
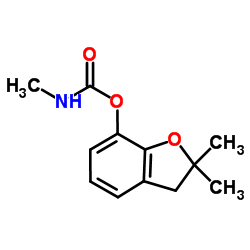 |
Carbofuran
CAS:1563-66-2 |
|
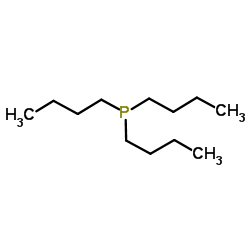 |
Tributylphosphine
CAS:998-40-3 |
|
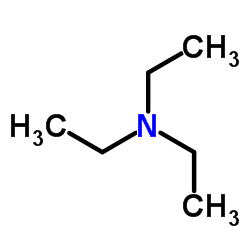 |
Triethylamine
CAS:121-44-8 |