| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
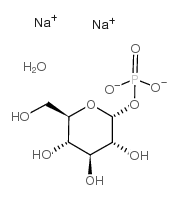 |
alpha-d-glucose-1-phosphate na2-salt
CAS:56401-20-8 |
|
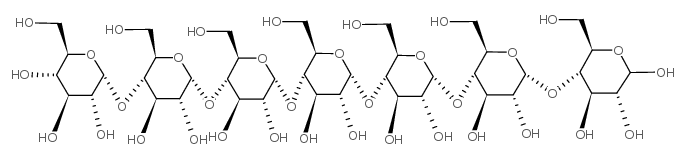 |
Maltoheptaose
CAS:34620-78-5 |