| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
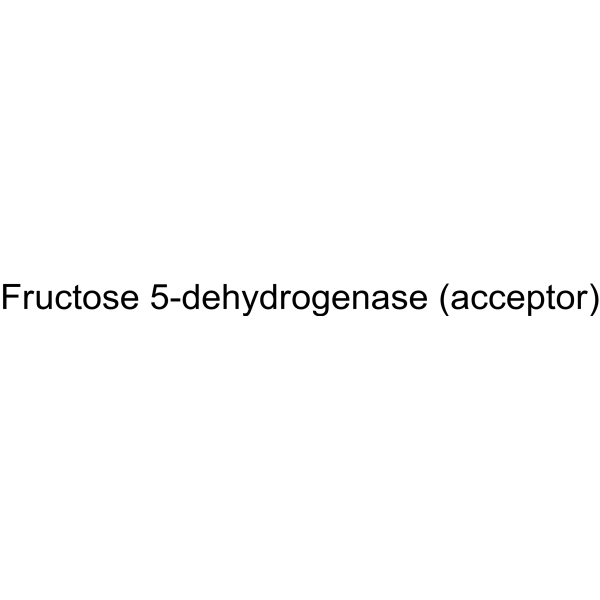 |
D-Fructose Dehydrogenase
CAS:37250-85-4 |
|
 |
Fructose
CAS:57-48-7 |