Further study on the 1,4-alpha-transglucosylation of rubusoside, a sweet steviol-bisglucoside from Rubus suavissimus.
K Ohtani, Y Aikawa, H Ishikawa, R Kasai, S Kitahata, K Mizutani, S Doi, M Nakaura, O Tanaka
Index: Agric. Biol. Chem. 55(2) , 449-53, (1991)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Rubusoside (the beta-D-glucosyl ester of 13-O-beta-D-glucosyl-steviol), which is the major sweet principle of leaves of Rubus suavissimus S. Lee, was subjected to 1,4-alpha-transglucosylation by the cyclodextringlucanotransferase-starch system (the CGTase system). The tri- and tetra-glucosylated products were isolated together with the mono- and di-glucosylated products, which had already been isolated. A prominent increase in intensity of the sweetness was observed for the compounds which were di- and tri-glucosylated at the 13-O-glucosyl moiety. This result further substantiated the structure-sweetness relationship for 1,4-alpha-glucosylated compounds of steviol-glycosides reported previously. For protection of the 19-COO-glucosyl moiety against glucosylation by the CGTase system, the 4-hydroxyl group of the 19-COO-glucosyl moiety was beta-galactosylated by the beta-galactosidase-lactose system. This galactosylated compound was subjected to a regio-selective glucosylation of the 13-O-glucosyl moiety by the CGTase system, which was followed by enzymic elimination of the galactosyl group to furnish an exclusive preparation of the improved sweeteners just mentioned.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
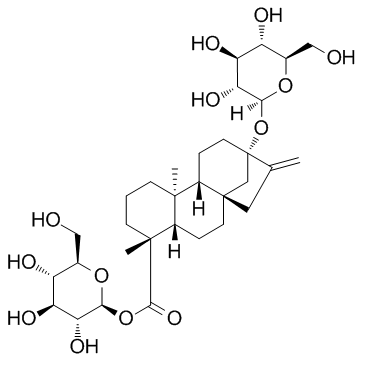 |
Rubusoside
CAS:64849-39-4 |
C32H50O13 |
|
Cytotoxic and antiangiogenic paclitaxel solubilized and perm...
2015-02-01 [Anticancer Drugs 26(2) , 167-79, (2014)] |
|
[Identification and biotransformation properties of a bacter...
2011-01-01 [Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao 51(1) , 43-9, (2011)] |
|
[Study on quality control of Rubus suavissimus].
2008-11-01 [Zhong Yao Cai 31(11) , 1734-7, (2008)] |
|
Mass spectral analysis of some derivatives and in vitro meta...
1988-02-15 [Biomed. Environ. Mass Spectrom. 15(4) , 211-22, (1988)] |
|
Quantitative and fingerprint analyses of Chinese sweet tea p...
2009-02-11 [J. Agric. Food Chem. 57(3) , 1076-83, (2009)] |