beta-NAD is a novel nucleotide released on stimulation of nerve terminals in human urinary bladder detrusor muscle.
Leanne T Breen, Lisa M Smyth, Ilia A Yamboliev, Violeta N Mutafova-Yambolieva
Index: Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 290(2) , F486-95, (2006)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Endogenous nucleotides with extracellular functions may be involved in the complex neural control of human urinary bladder (HUB). Using HPLC techniques with fluorescence detection, we observed that in addition to ATP and its metabolites ADP, AMP and adenosine, electrical field stimulation (EFS; 4-16 Hz, 0.1 ms, 15 V, 60 s) of HUB detrusor smooth muscle coreleases novel nucleotide factors, which produce etheno-1N(6)-ADP-ribose (eADPR) on etheno-derivatization at high temperature. A detailed HPLC fraction analysis determined that nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (beta-NAD+; 7.0 +/- 0.7 fmol/mg tissue) is the primary nucleotide that contributes to the formation of eADPR. The tissue superfusates collected during EFS also contained the beta-NAD+ metabolite ADPR (0.35 +/- 0.2 fmol/mg tissue) but not cyclic ADPR (cADPR). HUB failed to degrade nicotinamide guanine dinucleotide (NGD+), a specific substrate of ADP ribosyl cyclase, suggesting that the activity of this enzyme in the HUB is negligible. The EFS-evoked release of beta-NAD+ was frequency dependent and is reduced in the presence of tetrodotoxin (TTX; 0.3 micromol/l), omega-conotoxin GVIA (50 nmol/l), and botulinum neurotoxin A (BoNT/A; 100 nmol/l), but remained unchanged in the presence of guanethidine (3 micromol/l), omega-agatoxin IVA (50 nmol/l), or charbachol (1 micromol/l). Capsaicin (10 micromol/l) increased both the resting and EFS-evoked overflow of beta-NAD+. Exogenous beta-NAD+ (1 micromol/l) reduced both the frequency and amplitude of spontaneous contractions. In conclusion, we detected nerve-evoked overflow of beta-NAD+ and ADPR in HUB. The beta-NAD(+)/ADPR system may constitute a novel inhibitory extracellular nucleotide mechanism of neural control of the human bladder.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
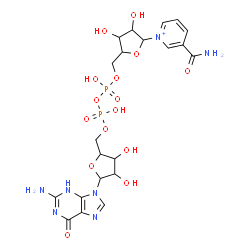 |
nicotinamide guanine dinucleotide sodium salt
CAS:5624-35-1 |
C21H27N7O15P2 |
|
ADP-ribosyl cyclase and GDP-ribosyl cyclase activities are n...
2005-11-15 [Anal. Biochem. 346(2) , 336-8, (2005)] |
|
Localization of the cyclic ADP-ribose-dependent calcium sign...
2007-03-01 [Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 48 , 978-984, (2007)] |
|
Purification and partial characterization of a novel phospho...
2011-09-01 [Biochimie 93 , 1601-1619, (2011)] |
|
Catalytic properties of the retinal rod outer segment disk A...
2011-03-01 [Vis. Neurosci. 28 , 121-128, (2011)] |
|
The CD38-independent ADP-ribosyl cyclase from mouse brain sy...
2006-04-15 [Biochem. J. 395(2) , 417-26, (2006)] |