| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
N-Isopropylacrylamide
CAS:2210-25-5 |
|
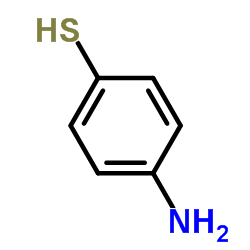 |
4-Aminothiophenol
CAS:1193-02-8 |