| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
a-methyl-D-phenylalanine
CAS:17350-84-4 |
|
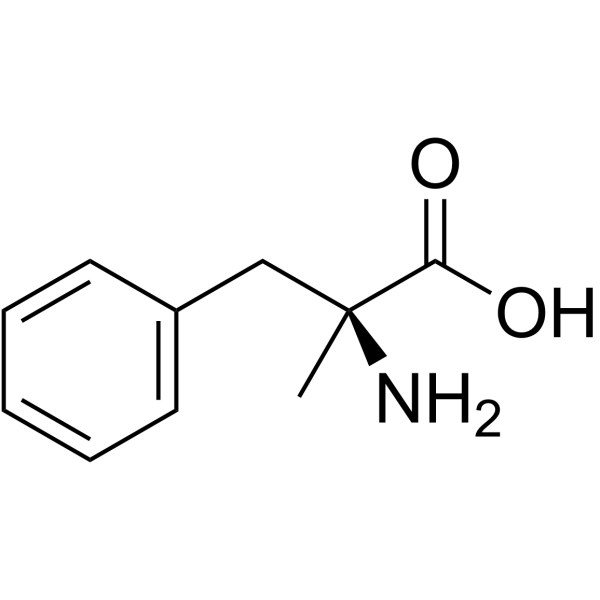 |
a-methyl-L-phenylalanine
CAS:23239-35-2 |
|
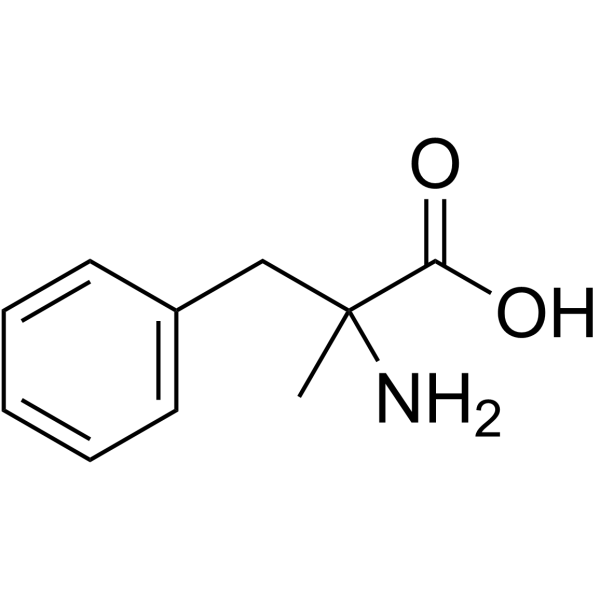 |
2-Amino-2-methyl-3-phenylpropionic acid
CAS:1132-26-9 |