Efficacy of pyrazolopyrimidine ribonucleosides against Trypanosoma cruzi: studies in vitro and in vivo with sensitive and resistant strains.
R L Berens, J J Marr, D L Looker, D J Nelson, S W LaFon
Index: J. Infect. Dis. 150(4) , 602-8, (1984)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Strains of Trypanosoma cruzi differ in their susceptibilities to and metabolism of pyrazolopyrimidines. Allopurinol riboside can control but not eliminate infections with a sensitive strain in both tissue culture and mice. Formycin B, which proved to be greater than 10-fold more effective on a weight basis, showed a similar strain specificity but could eliminate an infection with a sensitive strain from tissue culture. However, this drug, unlike allopurinol riboside, was converted to toxic analogues of adenosine mono-, di-, and triphosphate by uninfected tissue culture cells. Thiopurinol and its riboside were effective against all strains unless culture was performed in purine-defined medium. Thus formycin B and allopurinol riboside appear to be good models for the design of antitrypanosomal agents. Suitable modification of the molecule may provide an effective chemotherapeutic agent.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
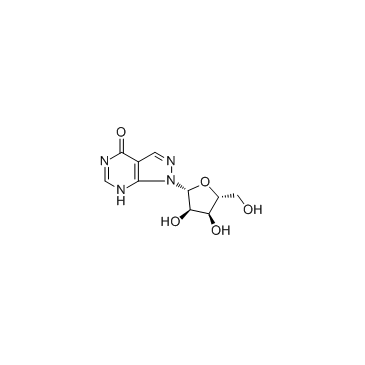 |
Allopurinol riboside
CAS:16220-07-8 |
C10H12N4O5 |
|
Activity of inosine analogs against Pneumocystis carinii in ...
1986-07-01 [Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 30(1) , 181-3, (1986)] |
|
A tissue culture system for the growth of several species of...
1988-03-01 [Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 38(2) , 304-7, (1988)] |
|
On the metabolism of allopurinol. Formation of allopurinol-1...
1983-07-15 [Biochem. Pharmacol. 32(14) , 2167-74, (1983)] |
|
Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of allopurinol riboside.
1991-05-01 [Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 49(5) , 506-14, (1991)] |
|
In vitro antileishmanial activity of inhibitors of steroid b...
1987-06-01 [J. Parasitol. 73(3) , 671-3, (1987)] |