| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
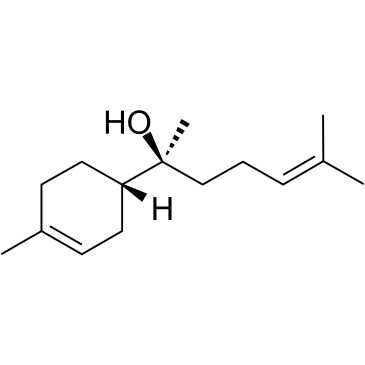 |
levomenol
CAS:23089-26-1 |
|
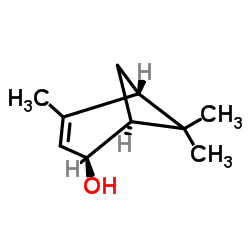 |
(S)-cis-Verbenol
CAS:18881-04-4 |