Measurement of thiol-containing amino acids and phytochelatin (PC2) via capillary electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence detection.
Jonathan J Hart, Ross M Welch, Wendell A Norvell, Leon V Kochian
Index: Electrophoresis 23(1) , 81-7, (2002)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
An analytical method for determining thiols and phytochelatins using high-performance capillary electrophoresis coupled with laser-induced fluorescence detection is presented. The technique utilizes the labeling of thiols with the fluorescent reagent 5-bromomethylfluorescein (5-BMF), which is excited by a 488 nm argon ion laser and fluoresces at 515 nm. The paper describes the determination of the optimal conditions for reaction of 5-BMF with thiols as well as the parameters for electrophoresis runs that produce optimal electropherogram peaks. The technique is shown to be very sensitive for cysteine, cysteinyl-glycine, gamma-glutamyl-cysteine, glutathione and (gamma-glutamylcysteinyl)2-glycine (PC2). Concentrations as low as 25 nmol/L and amounts as low as 1 fmol were detected for glutathione. Sensitivity for detection of PC2 was somewhat lower. The method was shown to be simple, rapid and accurate and should facilitate measurement of thiol-containing amino acids, peptides and phytochelatin (PC2) in small volumes of extracts obtained from biological tissue.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
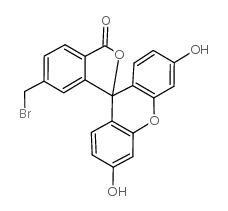 |
5-(Bromomethyl)fluorescein
CAS:148942-72-7 |
C21H13BrO5 |
|
Labeling the (Ca(2+)-Mg2+)-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum ...
1993-06-15 [Biochemistry 32 , 6095, (1993)] |
|
Effect of magnetic nanoparticles on tobacco BY-2 cell suspen...
2013-01-01 [Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 10 , 47-71, (2013)] |
|
Rapid long-range proton diffusion along the surface of the p...
1995-01-17 [Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 92(2) , 372-6, (1995)] |
|
5-Bromomethyl fluorescein (5-BMF) for derivatization of carb...
1995-06-01 [Pharm. Res. 12(6) , 930-6, (1995)] |
|
Analysis of gamma-(cholesteryloxy)butyric acid in biologic s...
1996-01-15 [Anal. Chem. 68(2) , 327-32, (1996)] |