Isolation and partial characterization of an extradiol non-haem iron dioxygenase which preferentially cleaves 3-methylcatechol.
M G Wallis, S K Chapman
Index: Biochem. J. 266(2) , 605-9, (1990)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
A purification procedure has been developed for an extradiol dioxygenase expressed in Escherichia coli, which was originally derived from a Pseudomonas putida strain able to grow on toluidine. Physical and kinetic properties of the enzyme have been investigated. The enzyme has a subunit Mr of 33,500 +/- 2000 by SDS/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Gel filtration indicates a molecular mass under non-denaturing conditions of 120,000 +/- 20,000. The N-terminal sequence (35 residues) of the enzyme has been determined and exhibits 50% identity with other extradiol dioxygenases. Fe(II) is a cofactor of the enzyme, as it is for other extradiol dioxygenases. The reactivity of this enzyme towards catechol and methyl-substituted catechols is somewhat different from that seen for other catechol 2,3-dioxygenases, with 3-methylcatechol cleaved at a higher rate than catechol or 4-methylcatechol. Km values for these substrates with this enzyme are all around 0.3 microM. The enzyme exhibits a bell-shaped pH profile with pKa values of 6.9 +/- 0.1 and 8.7 +/- 0.1. These results are compared with those found for other extradiol dioxygenases.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
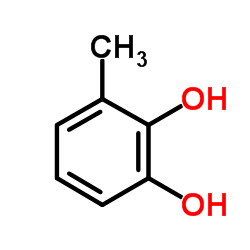 |
3-Methylcatechol
CAS:488-17-5 |
C7H8O2 |
|
Effects of plant species, stage of maturity, and level of fo...
2015-09-01 [J. Anim. Sci. 93 , 4408-23, (2015)] |
|
Characterization of catechol 2,3-dioxygenase from Planococcu...
2012-01-01 [Acta Biochim. Pol. 59(3) , 345-51, (2012)] |
|
Electrochemical synthesis of novel 1,3-indandione derivative...
2013-01-01 [Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 12 , 91-103, (2013)] |
|
Selection for growth on 3-nitrotoluene by 2-nitrotoluene-uti...
2015-01-01 [Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 81(1) , 309-19, (2014)] |
|
New insights on toluene biodegradation by Pseudomonas putida...
2007-03-01 [Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 74(4) , 857-66, (2007)] |