| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
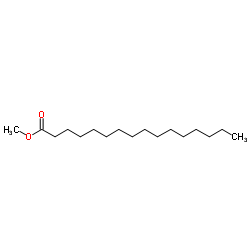 |
Methyl palmitate
CAS:112-39-0 |
|
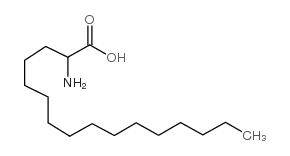 |
2-Aminohexadecanoic acid
CAS:7769-79-1 |