| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
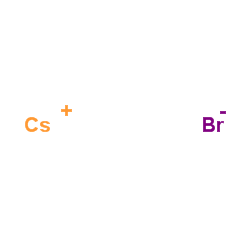 |
Cäsiumbromid
CAS:7787-69-1 |
|
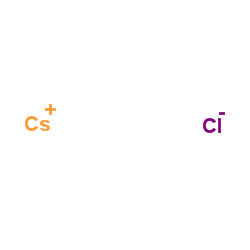 |
Cesium chloride
CAS:7647-17-8 |
|
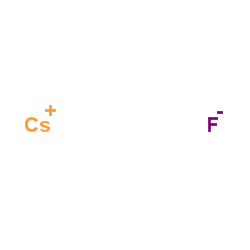 |
Caesium fluoride
CAS:13400-13-0 |