| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Galactose oxidase
CAS:9028-79-9 |
|
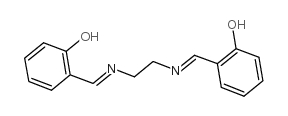 |
n,n'-bis(salicylidene)ethylenediamine
CAS:94-93-9 |