| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
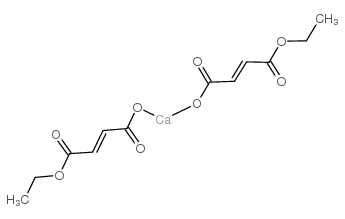 |
calcium; (E)-4-ethoxy-4-oxo-but-2-enoic acid; hydrogen(-1) anion
CAS:62008-22-4 |
|
 |
1,2,4,5-Tetramethylbenzene
CAS:95-93-2 |
|
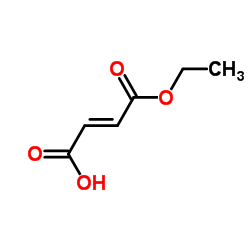 |
Monoethyl fumarate
CAS:2459-05-4 |