Case histories of bald eagles and other raptors killed by organophosphorus insecticides topically applied to livestock.
C J Henny, E J Kolbe, E F Hill, L J Blus
Index: J. Wildl. Dis. 23(2) , 292-5, (1987)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Since 1982 when secondary poisoning of a red-tailed hawk (Buteo jamaicensis) was documented following the recommended use of famphur applied topically to cattle, the Patuxent Wildlife Research Center has tested dead birds of prey for poisoning by famphur and other pour-on organophosphorus (OP) insecticides. Brain cholinesterase (ChE) activity was first determined, then if ChE was depressed greater than or equal to 50%, stomach and/or crop contents were evaluated for anti-ChE compounds. This report presents the circumstances surrounding the OP-caused deaths of eight bald eagles (Haliaeetus leucocephalus), two red-tailed hawks, and one great horned owl (Bubo virginianus) between March 1984 and March 1985. OP poisoning of raptors by pour-on insecticides in the United States is widespread, but its magnitude is unknown.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
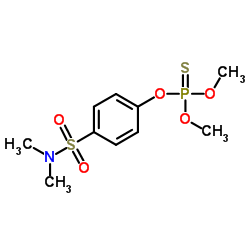 |
American Cyanamid 38023
CAS:52-85-7 |
C10H16NO5PS2 |
|
Development of phage immuno-loop-mediated isothermal amplifi...
2014-08-19 [Anal. Chem. 86(16) , 8441-7, (2014)] |
|
Prediction for the mixture toxicity of six organophosphorus ...
2008-11-01 [Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 71(3) , 880-8, (2008)] |
|
Systemic control of cattle grubs (Hypoderma spp.) in steers ...
1981-01-01 [Can. J. Comp. Med. 45(1) , 15-9, (1981)] |
|
Local and systemic reactions in cattle to Hypoderma lineatum...
1981-01-01 [Am. J. Vet. Res. 42(1) , 25-8, (1981)] |
|
Presumptive organophosphate-induced delayed neurotoxicity in...
1985-07-01 [Cornell Vet. 75(3) , 401-10, (1985)] |