Lack of alachlor induced DNA damage as assayed in rodent liver by the alkaline elution test.
M Taningher, M P Terranova, L Airoldi, L Chiappetta, S Parodi
Index: Toxicology 85(2-3) , 117-22, (1993)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Alachlor was studied in vivo for its capability to induce DNA damage, as evaluated by the alkaline elution test. The experiments were performed in mouse and rat liver after acute or subacute intraperitoneal or per os administrations of the chemical at sublethal dosages. Rat liver was also studied for DNA damage after administration of 2,6-diethylaniline, one of alachlor's major metabolites. Eluted DNA from treated animals was indistinguishable from control DNA. The results show that neither alachlor nor its metabolite cause DNA damage as determined by the number of single strand breaks.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
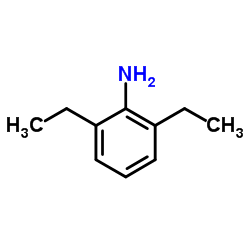 |
2,6-Diethylaniline
CAS:579-66-8 |
C10H15N |
|
Ferrocene-based guanidine derivatives: in vitro antimicrobia...
2014-10-06 [Eur. J. Med. Chem. 85 , 438-49, (2014)] |
|
Further evidence of an inverted region in proton transfer wi...
2006-05-25 [J. Phys. Chem. A 110(20) , 6408-14, (2006)] |
|
Spectroscopic studies of molecular interactions involving 2,...
2007-01-01 [Spectrochim. Acta. A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 66(1) , 94-101, (2007)] |
|
Biodegradation of alachlor by soil streptomycetes.
2004-06-01 [Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 64(5) , 712-7, (2004)] |
|
Determination of alachlor and its metabolite 2,6-diethylanil...
2011-08-10 [J. Agric. Food Chem. 59(15) , 8078-85, (2011)] |