The fate of 4-cyano-N,N-dimethylaniline in mice: the occurrence of a novel metabolite during N-demethylation of an aromatic amine.
C J Logan, D H Hutson, D Hesk
Index: Xenobiotica 15(5) , 391-7, (1985)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
4-Cyano-N,N-dimethylaniline (CDA), when administered as a single oral dose to mice (18.5 mg/kg), was rapidly absorbed and eliminated. The major route of elimination was the urine (78% dose in 24h). The residues in the tissues 48 h after dosing, as microgram equiv. of CDA/g, were: liver, 0.19; kidney, 0.10; testes, 0.01; fat, 0.10; blood, 0.02. The major metabolite was 2-amino-5-cyanophenyl sulphate, with the N-methyl analogue as a minor metabolite. A novel metabolite, N-acetyl-S-(4-cyanoanilinomethyl)cysteine, was also a significant urinary metabolite, indicating that an electrophilic intermediate is generated during the N-demethylation of CDA. The implications are that N-demethylation may have important toxicological consequences.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
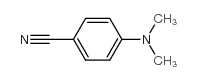 |
4-Dimethylaminobenzonitrile
CAS:1197-19-9 |
C9H10N2 |
|
Predicting the carcinogenicity of the aromatic amine derivat...
1986-03-01 [Mutagenesis 1(2) , 119-23, (1986)] |
|
The formation of a novel mercapturic acid during the metabol...
1984-07-15 [Biochem. Pharmacol. 33(14) , 2345-6, (1984)] |
|
Computer-automated prediction of the mutagenicity of benzidi...
1986-07-01 [Mutagenesis 1(4) , 275-82, (1986)] |
|
The fate of 4-cyano-N,N-dimethylaniline in rats; a novel inv...
1984-12-01 [Xenobiotica 14(12) , 925-34, (1984)] |
|
Presence and absence of excited state intramolecular charge ...
2011-10-13 [J. Phys. Chem. A 115(40) , 10823-45, (2011)] |