The comparative metabolism of diisopropyl methylphosphonate in mink and rats.
D J Weiss, R S Geary, W Wustenberg, T J Bucci, V Perman, I P Baumel, J C Dacre
Index: Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 27(3) , 420-5, (1994)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
This study reports the metabolism of carbon-14labeled diisopropyl methylphosphonate (DIMP) in mink and rats, undertaken to better understand the dose-related mortality reported for mink in a previous study. In both male and female mink and rats, DIMP was rapidly absorbed after oral administration; it was metabolized by a saturable pathway to a single metabolite, isopropyl methylphosphonate (IMPA), which was rapidly excreted, primarily in the urine (90%). Fecal radioactivity, also identified as IMPA, was 1.7-3.1% of the administered dose. Female rats had a slower rate of conversion of DIMP to IMPA and less total excretion of IMPA than male rats. Metabolism of DIMP administered intravenously was not very different from that given orally in both species. These data indicate that mink absorb, metabolize, and excrete DIMP (as IMPA) in a manner very similar to mice, rats, and dogs.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
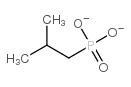 |
Isopropyl methylphosphonic acid
CAS:1832-54-8 |
C4H9O3P-- |
|
Fluctuating asymmetry and condition in golden shiner (Notemi...
2006-01-01 [Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 25(1) , 58-64, (2006)] |
|
Acute toxicity of isopropyl methylphosphonic acid, a breakdo...
2005-01-22 [J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 68(2) , 141-9, (2005)] |
|
Study proves Iraq used nerve gas.
1993-05-06 [Nature 363(6424) , 3, (1993)] |
|
Electro membrane isolation of nerve agent degradation produc...
2008-12-19 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1214(1-2) , 17-22, (2008)] |
|
Ion-pair liquid-liquid-liquid microextraction of nerve agent...
2008-09-26 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1205(1-2) , 158-62, (2008)] |