Recent advances in the biodegradation of chlorothalonil.
Guangli Wang, Bin Liang, Feng Li, Shunpeng Li
Index: Curr. Microbiol. 63(5) , 450-7, (2011)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Chlorothalonil (TPN; 2,4,5,6-tetrachloroisophthalonitrile) has been widely used as a broad-spectrum chlorinated aromatic fungicide and its application resulted in global pollution commonly detected in the diverse ecosystems. Recently, microbial degradation of TPN has been studied extensively as an effective and environmental-friendly method to reduce TPN residue levels in the environment. This review summarizes the current knowledge of recent developments in the biodegradation of TPN. Diverse pure culture strains capable of degrading TPN were widely distributed among Proteobacteria and several metabolic pathways of TPN biotransformation were discovered. The two key genes (glutathione S-transferase and chlorothalonil hydrolytic dehalogenase coding gene) responsible for the conversion of TPN and recent findings for future practical bioremediation of TPN-contaminated ecosystem are also discussed.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
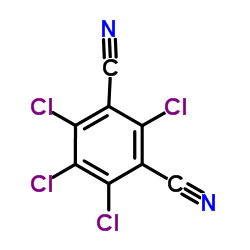 |
Chlorothalonil
CAS:1897-45-6 |
C8Cl4N2 |
|
Effects of seven antifouling compounds on photosynthesis and...
2012-10-01 [Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 63(3) , 365-77, (2012)] |
|
Development and validation of one-step ultrasound-assisted e...
2015-01-01 [J. AOAC Int. 98(1) , 192-200, (2015)] |
|
Photoreduction of chlorothalonil fungicide on plant leaf mod...
2011-11-15 [Environ. Sci. Technol. 45(22) , 9582-9, (2011)] |
|
Measuring Leaf Penetration and Volatilization of Chlorothalo...
2015-11-01 [J. Environ. Qual. 44 , 1782-90, (2015)] |
|
Washing effects of limonene on pesticide residues in green p...
2013-09-01 [J. Sci. Food Agric. 93(12) , 2917-21, (2013)] |