Enzyme catalyzed electricity-driven water softening system.
Mary A Arugula, Kristen S Brastad, Shelley D Minteer, Zhen He
Index: Enzyme Microb. Technol. 51(6-7) , 396-401, (2012)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Hardness in water, which is caused by divalent cations such as calcium and magnesium ions, presents a major water quality problem. Because hard water must be softened before use in residential applications, there is great interest in the saltless water softening process because, unlike ion exchange softeners, it does not introduce additional ions into water. In this study, a saltless hardness removal driven by bioelectrochemical energy produced through enzymatic oxidation of glucose was proposed and investigated. Glucose dehydrogenase was coated on a carbon electrode to catalyze glucose oxidation in the presence of NAD⁺ as a cofactor/mediator and methylene green as an electrocatalyst. The results showed that electricity generation stimulated hardness removal compared with non-electricity conditions. The enzymatic water softener worked upon a 6h batch operation per day for eight days, and achieved an average hardness removal of 46% at a high initial concentration of 800 mg/L as CaCO₃. More hardness was removed at a lower initial concentration. For instance, at 200mg/L as CaCO₃ the enzymatic water softener removed 76.4±4.6% of total hardness. The presence of magnesium ions decreased hardness removal because of its larger hydrated radius than calcium ions. The enzymatic water softener removed 70-80% of total hardness from three actual hard water samples. These results demonstrated a proof-of-concept that enzyme catalyzed electricity generation can be used to soften hard water.Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
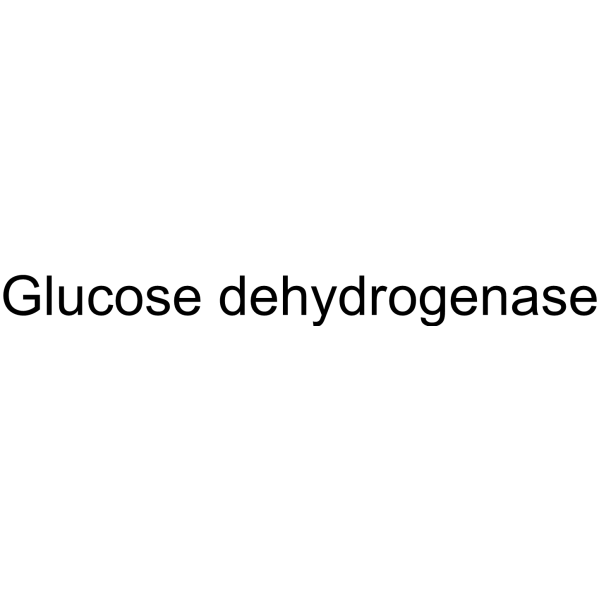 |
ec 1.1.1.47
CAS:9028-53-9 |
|
Characterization of the low-temperature activity of Sulfolob...
2014-10-01 [J. Biosci. Bioeng. 118(4) , 367-71, (2014)] |
|
Repression of oxalic acid-mediated mineral phosphate solubil...
2013-02-01 [Arch. Microbiol. 195(2) , 81-8, (2013)] |
|
Direct electron transfer type disposable sensor strip for gl...
2013-02-05 [Enzyme Microb. Technol. 52(2) , 123-8, (2013)] |
|
Increased pheromone cCF10 expression in Enterococcus faecali...
1998-04-01 [Curr. Microbiol. 65(6) , 656-9, (2012)] |
|
Glucose dehydrogenase from pig liver. I. Isolation and purif...
1970-03-18 [Biochim. Biophys. Acta 198(3) , 397-406, (1970)] |