Simple and rapid method for the analysis of phenolic compounds in beverages and grains.
Marjorie B Medina
Index: J. Agric. Food Chem. 59(5) , 1565-71, (2011)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
A new method for the detection of phenolics in food systems was developed. This method is based on interactions of phenolics with Fast Blue BB diazonium salt in alkali pH, forming azo complexes, with the absorbance measured at 420 nm after 60 min. The linear regression correlations (R(2)) of gallic acid calibration standards were >0.99. The phenolic content (gallic acid equivalent) of samples analyzed yielded higher ratios (1.7-6.6) of the total phenolics by Fast Blue BB to Folin-Ciocalteu methods in most beverages and grain samples, but in flaxseed and some juice blends, the ratios were <1. The lower ratios suggest the presence of non-phenolic reducing constituents measured with the Folin-Ciocalteu method as "total phenolics". This method is simple and inexpensive and can be used to rapidly assess the total phenolics of foods and beverages.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
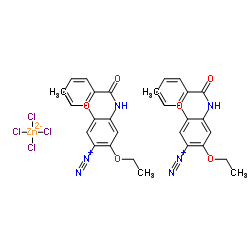 |
Fast Blue BB salt
CAS:5486-84-0 |
C34H36Cl4N6O6Zn |
|
Ratjadone C-mediated nuclear accumulation of HDAC4: implicat...
2014-01-01 [Z. Naturforsch., C, J. Biosci. 69(11-12) , 471-8, (2015)] |
|
Ultrastructural cytochemistry of non-specific esterase in mu...
1989-05-01 [Histochem. J. 21(5) , 301-8, (1989)] |
|
Analysis of mast cell subpopulations (MCT, MCTC) in cutaneou...
1994-12-01 [Exp. Dermatol. 3(6) , 290-7, (1994)] |
|
[Screening of endophytic fungi from Huperzia serrata for ace...
2012-12-01 [Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 37(24) , 3701-5, (2012)] |
|
Determination of rat plasma esterase-1 (ES-1) activity by sc...
1991-12-01 [Electrophoresis 12(12) , 1045-50, (1991)] |