| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
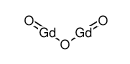 |
Gadolinium oxide
CAS:12064-62-9 |
|
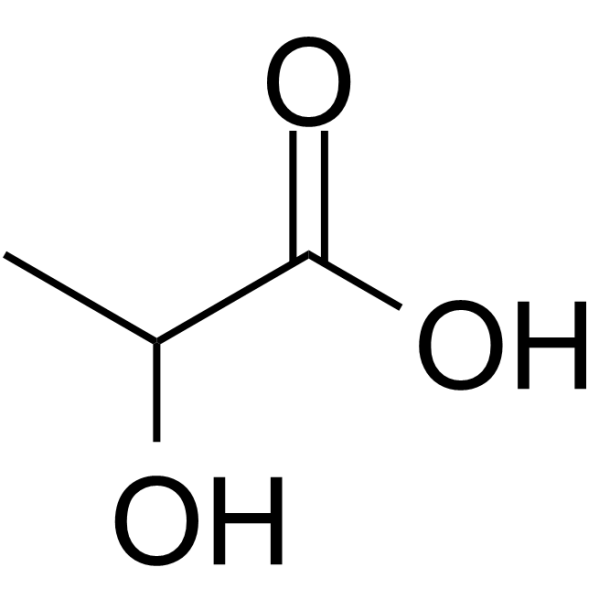 |
Lactic acid
CAS:50-21-5 |
|
 |
Gadolinium
CAS:7440-54-2 |