Stent-based tempamine delivery on neointimal formation in a porcine coronary model.
Yanming Huang, Lan Wang, Shengqiao Li, Xiaoshun Liu, Kwangdeok Lee, Eric Verbeken, Frans van de Werf, Ivan de Scheerder
Index: Acute Card. Care 8(4) , 210-6, (2006)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Tempamine is one of new class of antioxidant agents, the nitroxides, which have shown a wide range of biological effects like suppressing free radical driven reactions to maintain cell functions. The objectives of this study were to evaluate the effect of a biodegradable polymer coated stent loaded with tempamine on in-stent neointimal formation.Stainless steel stents were dip coated in biodegradable elastomeric poly (ester-amide) (co-PEA) or in polymer solution mixed with 50% (wt%) and 100% (wt%) tempamine. One group 100% (wt%) tempamine loaded stents were further dip coated in co-PEA polymer to form a top layer. Stainless steel bare, polymer-only, and different doses tempanine coated stents were implanted into porcine coronary arteries with a stent to artery ratio 1.2:1. Histomorphometric analysis was performed at 5 days and 6 weeks respectively.Histomorphometric analysis showed that the bare, polymer-only and tempamine-coated stents elicited a similar tissue response at 5 days. At 6 weeks, the peri-strut inflammation and neointimal hyperplasia of polymer-only stents were comparable to the bare stents. Compared to the bare stents, 50% tempanine coated stents had a trend to decrease the arterial injury (0.62 +/- 0.41 versus 0.34 +/- 0.18, P = 0.075) and neointimal hyperplasia (1.80 +/- 0.77 versus 1.27 +/- 0.39 mm2, P = 0.085). However, 100% tempanine coated showed significantly increased inflammatory response and neointimal formation.These co-PEA polymer coatings showed a biocompatible performance. Loaded with 50% tempamine had a trend to decrease neointimal hyperplasia. The 100% tempamine for stent-based delivery may have potential cytotoxic effects to arterial wall. Using a co-PEA polymer topcoat could effectively abolish these side effects.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
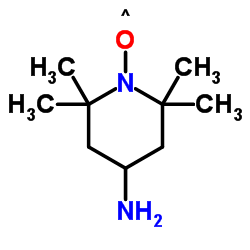 |
4-amino-tempo
CAS:14691-88-4 |
C9H19N2O |
|
Synthesis of Nanogels via Cell Membrane-Templated Polymeriza...
2015-09-09 [Small 11 , 4309-13, (2015)] |
|
Design and synthesis of digitally encoded polymers that can ...
2015-01-01 [Nat. Commun. 6 , 7237, (2015)] |
|
Different effectiveness of piperidine nitroxides against oxi...
2008-01-01 [Cell Biol. Toxicol. 24(1) , 101-12, (2008)] |
|
Ion exchange in alginate gels--dynamic behaviour revealed by...
2015-12-14 [Soft Matter 11 , 8968-74, (2015)] |
|
Probing the antimalarial mechanism of artemisinin and OZ277 ...
2010-03-01 [Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 54 , 1042-6, (2010)] |