| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
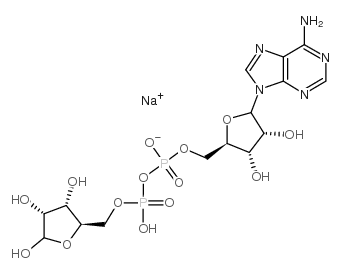 |
Adenosine 5′-diphosphoribose sodium
CAS:68414-18-6 |
|
 |
DL-Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
CAS:591-59-3 |
|
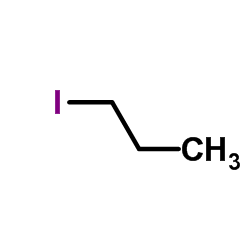 |
1-Iodopropane
CAS:107-08-4 |
|
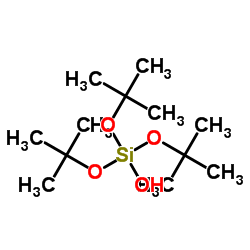 |
Tris(2-methyl-2-propanyl) hydrogen orthosilicate
CAS:18166-43-3 |