Confirmation of D-aspartic acid in the novel dipeptide beta-aspartylglycine isolated from tissue extract of Aplysia kurodai.
M Sato, T Yamaguchi, N Kanno, Y Sato
Index: Biochem. J. 263(2) , 617-20, (1989)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
A novel o-phthalaldehyde-reactive compound was found in the h.p.l.c. chromatogram of Aplysia kurodai extract. This compound was isolated by ion-exchange chromatography and preparative high-voltage paper electrophoresis. It was shown by optical-rotatory-dispersion spectrum and optical-resolution h.p.l.c. analysis that this compound consisted of equimolar amounts of D-aspartic acid and glycine. This compound resisted cleavage in the Edman reaction. This peptide was inferred to be beta-D-aspartylglycine, and this was confirmed by synthesis. beta-D-Aspartylglycine was detected in all tissues of Aplysia kurodai, with especially high concentrations in body wall (skin and muscle) and gill.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
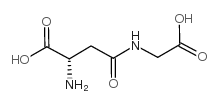 |
H-Asp(Gly-OH)-OH
CAS:3790-52-1 |
C6H10N2O5 |
|
'Normalization' of germfree mice after direct and indirect c...
1986-10-01 [Lab. Anim. 20(4) , 286-90, (1986)] |
|
Influence of zinc bacitracin and Bacillus licheniformis on m...
2003-10-01 [Vet. Res. Commun. 27(7) , 513-26, (2003)] |
|
[Rapid diagnosis of dysbacteriosis by detecting beta-asparty...
1985-08-01 [Zh. Mikrobiol. Epidemiol. Immunobiol. (8) , 15-8, (1985)] |
|
Effects of selective oral antimicrobial prophylaxis and syst...
1989-08-01 [APMIS 97(8) , 705-14, (1989)] |
|
[Changes in the microflora of the large intestine in rats ad...
1987-03-01 [Antibiot. Med. Biotekhnol. 32(3) , 206-10, (1987)] |