Synthesis of the novel dipeptide beta-aspartylglycine by Aplysia ganglia.
M W McCaman, J Stetzler
Index: J. Neurochem. 45(3) , 983-6, (1985)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Isolated ganglia from Aplysia californica rapidly took up [14C]glycine or [14C]aspartate from a sea-water medium. Approximately 20% of the tissue radioactivity was recovered in the peptides beta-aspartylglycine and glutathione after incubation with [14C]glycine. Compared with other individual cells isolated from the abdominal ganglion, the glycine-containing white cells (R3-R14) incorporated less [14C]glycine into beta-aspartylglycine, but similar amounts into glutathione. In contrast, [14C]aspartate was metabolized primarily to nonamino dicarboxylic acids and relatively little radioactivity was incorporated into beta-aspartylglycine.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
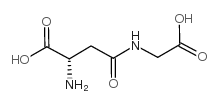 |
H-Asp(Gly-OH)-OH
CAS:3790-52-1 |
C6H10N2O5 |
|
'Normalization' of germfree mice after direct and indirect c...
1986-10-01 [Lab. Anim. 20(4) , 286-90, (1986)] |
|
Influence of zinc bacitracin and Bacillus licheniformis on m...
2003-10-01 [Vet. Res. Commun. 27(7) , 513-26, (2003)] |
|
[Rapid diagnosis of dysbacteriosis by detecting beta-asparty...
1985-08-01 [Zh. Mikrobiol. Epidemiol. Immunobiol. (8) , 15-8, (1985)] |
|
Effects of selective oral antimicrobial prophylaxis and syst...
1989-08-01 [APMIS 97(8) , 705-14, (1989)] |
|
[Changes in the microflora of the large intestine in rats ad...
1987-03-01 [Antibiot. Med. Biotekhnol. 32(3) , 206-10, (1987)] |