Haemoglobin adducts of aromatic amines in people exposed to cigarette smoke.
M S Bryant, P Vineis, P L Skipper, S R Tannenbaum
Index: IARC Sci. Publ. (89) , 133-6, (1988)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
In a population-based study in Turin, Italy, smokers of blond tobacco showed 4-aminobiphenyl (4-ABP) adduct levels some three times higher than nonsmoking subjects, and smokers of black tobacco showed levels about five times greater than nonsmokers. A dose-response relationship between the number of cigarettes smoked per day and 4-ABP adduct level was observed, but did not account for the higher adduct levels observed in smokers of black tobacco. Smoking-related increases in haemoglobin adducts were also observed for o-toluidine, p-toluidine, 2,4-dimethylaniline and 2-ethylaniline. Smoking subjects showed 3-aminobiphenyl adduct levels about 12 times greater than those of nonsmokers, who rarely showed a detectable level. This may indicate that there are fewer sources of 3-aminobiphenyl exposure not related to tobacco smoke. Smokers of black tobacco showed higher adduct levels than smokers of blond tobacco for 4-ABP, p-toluidine and 2,4-dimethylaniline.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
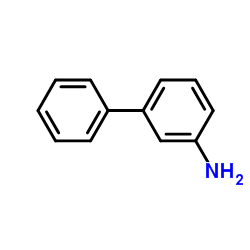 |
3-Biphenylamine
CAS:2243-47-2 |
C12H11N |
|
Hemoglobin adducts of aromatic amines: associations with smo...
1988-12-01 [Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 85(24) , 9788-91, (1988)] |
|
Elevated blood levels of carcinogens in passive smokers.
1989-10-01 [Am. J. Public Health 79(10) , 1381-4, (1989)] |
|
Nonsmoking-related arylamine exposure and bladder cancer ris...
2003-06-01 [Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 12(6) , 503-7, (2003)] |
|
Haemoglobin adducts formed by aromatic amines in smokers: so...
1990-04-01 [Br. J. Cancer 61(4) , 534-7, (1990)] |
|
Carotenoids/vitamin C and smoking-related bladder cancer.
2004-06-20 [Int. J. Cancer 110(3) , 417-23, (2004)] |