| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
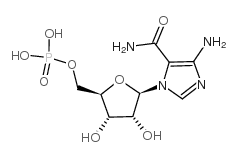 |
Aica ribonucleotide
CAS:3031-94-5 |
|
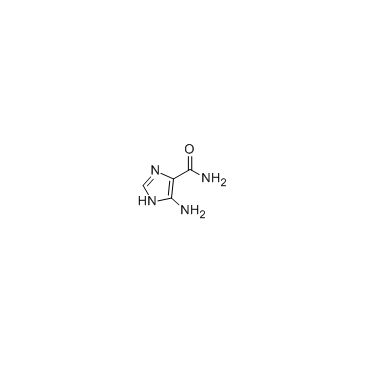 |
5-Amino-4-imidazolecarboxamide
CAS:360-97-4 |
|
 |
Lipoteichoic Acid
CAS:56411-57-5 |