An in vitro investigation of two currently marketed dentin tubule occlusion dentifrices.
Charles R Parkinson, Richard J Willson
Index: J. Clin. Dent. 22(1) , 6-10, (2011)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The objective of this study was to evaluate the relative level of dentin tubule occlusion afforded by two dentifrices specifically developed to occlude dentin tubules, following finger-applied dab-on application and by repeated brushing, in a longitudinal acid-challenge-based dentin disk model. The impact of a dietary acid alone (grapefruit juice) on the level of dentin tubule occlusion conferred by each product following dab-on application was also explored in a separate short-term stand-alone exploratory dentin disk-based in vitro study.For the longitudinal study, 120 bovine dentin discs, polished and etched in citric acid for two minutes to provide a smooth dentin surface with patent tubules, were divided into three treatment groups and subjected to a finger application of the dentifrice only, or a combination of finger application and brushing. Prior to and between treatments, the dentin samples were stored in saliva (for > 60 minutes). The test products were an 8% w/w strontium acetate dentifrice (currently marketed as Sensodyne Rapid Relief), an arginine-based dentifrice (marketed as Colgate Sensitive Pro-Relief), and deionized water. For the exploratory acid resistance study, 24 dentin samples were divided into two treatment groups. Treatment consisted of a single dab-on application with the test dentifrices to the hydrated surface of dentin, followed by exposure to either a 30-second or 10-minute grapefruit juice acid challenge. For both models, at the end of each treatment period, the samples were removed for scanning electron microscopy analysis and graded on a categorical visual scale. All data were analyzed statistically by unpaired t-test comparison.In the longitudinal (four-day) model, the strontium acetate-based dentifrice occluded dentin tubules significantly better than the currently marketed arginine-based dentifrice post-dab-on treatment and grapefruit juice challenge (p < 0.0001). At all other time points, the strontium acetate dentifrice demonstrated significantly better occlusion than the arginine-based dentifrice (p < or = 0.0001). In the exploratory acid resistance model, the level of occlusion observed for the strontium acetate dentifrice was statistically significantly greater when compared to the arginine dentifrice following 10-second and 10-minute (p < 0.0001) exposures to grapefruit juice.A strontium acetate dentifrice is observed to deliver statistically significantly greater levels of dentin tubule occlusion when compared to the arginine dentifrice following dab-on and brushing application under dietary acid-challenge conditions in this in vitro model. This study suggests that the arginine-containing dentifrice may be more susceptible to acid-mediated dissolution than the strontium-based dentifrice under the conditions employed in this in vitro model.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
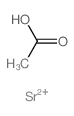 |
STRONTIUM ACETATE
CAS:543-94-2 |
C2H4O2Sr++ |
|
A novel method for local administration of strontium from im...
2010-05-01 [J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 21(5) , 1605-9, (2010)] |
|
An in situ study investigating dentine tubule occlusion of d...
2012-07-01 [J. Dent. 40(7) , 585-93, (2012)] |
|
Clinical efficacy in reducing dentin hypersensitivity of a d...
2011-01-01 [J. Clin. Dent. 22(4) , 128-38, (2011)] |
|
Comparative evaluation of the efficacy of three commercially...
2011-01-01 [J. Clin. Dent. 22(4) , 121-7, (2011)] |
|
Comparison of clinical efficacy of three toothpastes in redu...
2011-01-01 [J. Clin. Dent. 22(4) , 113-20, (2011)] |