Identification of the female-produced sex pheromone of the scarab beetle, Hoplia equina.
Aijun Zhang, Paul S Robbins, Anne L Averill, Donald C Weber, Charles E Linn, Wendell L Roelofs, Michael G Villani
Index: J. Chem. Ecol. 29(7) , 1635-42, (2003)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Hoplia equina LeConte (Coleoptera Scarabaeidae: Melolonthinae) is a beetle pest of cranberry beds in Massachusetts. Larvae feed on the roots of the cranberry plant, reducing yield as well as vine density. The female sex pheromone was identified as 2-tetradecanone. There were eight compounds found in the airborne volatiles collected from females that elicited antennal responses from males. Of the eight compounds tested (nonanal, decanal, dodecanal, 2-dodecanone, 2-tridecanone, 2-tetradecanone, 2-pentadecanone, and 2-hexadecanone), 2-tetradecanone was the only one that attracted male beetles in the field. Combining any of the other seven antennally active compounds with 2-tetradecanone did not increase male capture.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
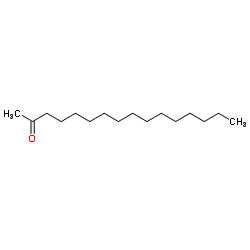 |
2-Hexadecanone
CAS:18787-63-8 |
C16H32O |
|
A glucose/hydrogen peroxide biofuel cell that uses oxidase a...
2002-05-15 [Bioelectrochemistry 56(1-2) , 99-105, (2002)] |
|
Cycloalkanones. 9. Comparison of analogues which inhibit cho...
1976-10-01 [J. Med. Chem. 19(10) , 1257-61, (1976)] |
|
Cycloalkanones. 8. Hypocholesterolemic activity of long-chai...
1976-02-01 [J. Med. Chem. 19(2) , 219-22, (1976)] |
|
Lipids in the femoral gland secretions of male Schreiber's g...
2006-01-01 [Z. Naturforsch., C, J. Biosci. 61(9-10) , 763-8, (2006)] |
|
Amperometric pH-sensing biosensors for urea, penicillin, and...
[Anal. Chim. Acta 415(1) , 151-157, (2000)] |