Increased folate catabolism following total body gamma-irradiation in mice.
Vellappan Kesavan, Madan S Pote, Vipen Batra, Gomathy Viswanathan
Index: J. Radiat. Res. 44(2) , 141-4, (2003)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Concentrations of total folates and their oxidative degradate, para-aminobenzoyl glutamic acid, were determined in mouse after 2-7 Gy total body gamma-irradiation (TBI). Total liver folate levels were drastically reduced by almost 47% over a period of 120 h after TBI with 7 Gy. Oxidative damage, splitting the folate molecule into pterin and p-aminobenzoylglutamic acid (p-ABG), was observed after TBI. p-ABG levels, which 24 h after irradiation were raised by 15%, were further elevated to more than three-fold over the control after 120 h. A dose-dependent increase in the oxidative degradation of folate was observed. The oxidative cleavage of folate may be one factor contributing to folate deficiency in radiation stress.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
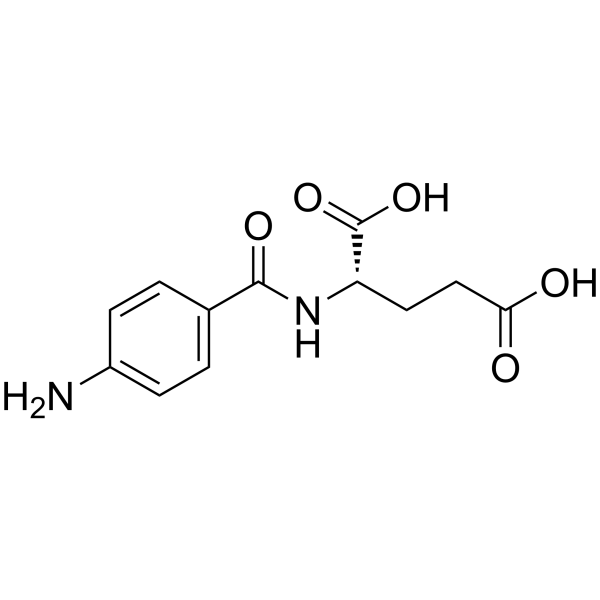 |
N-(4-aminobenzoyl)-L-glutamic acid
CAS:4271-30-1 |
C12H14N2O5 |
|
Simultaneous quantification of 21 water soluble vitamin circ...
2015-11-27 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1422 , 89-98, (2015)] |
|
Photodegradation of folic acid in aqueous solution.
1999-03-01 [J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 19 , 269-275, (1999)] |
|
Kinetic model of folate metabolism in nonpregnant women cons...
1998-11-01 [J. Nutr. 128(11) , 1896-906, (1998)] |
|
Purification and properties of a folate-catabolizing enzyme.
2000-11-10 [J. Biol. Chem. 275(45) , 35646-55, (2000)] |
|
Quantitation of folates and their catabolites in blood plasm...
2010-03-15 [Anal. Biochem. 398(2) , 150-60, (2010)] |