| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
N-Acetyl-DL-methionine
CAS:1509-92-8 |
|
 |
N-Acetyl-DL-methionine
CAS:1115-47-5 |
|
 |
N-acetyl-L-methionine
CAS:65-82-7 |
|
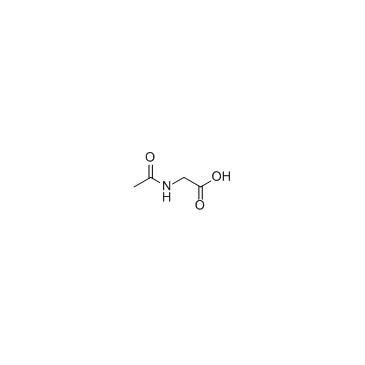 |
Ac-Gly-OH
CAS:543-24-8 |
|
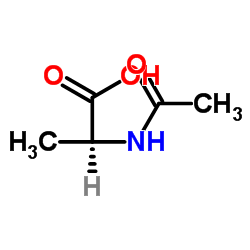 |
N-Acetyl-L-alanine
CAS:97-69-8 |