Influence of the morphology of poly(EGDMA-co-HEMA) on the chemical modifications and retention of O-phosphothreonine.
Cesar G Gomez, Cecilia I Alvarez, Miriam C Strumia, Cesar G. Gomez, Cecilia I. Alvarez, Miriam C. Strumia
Index: J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 55(1) , 23-36, (2003)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The influence of the morphology of ethylene glycol dimethacrylate-hydroxyethyl methacrylate copolymer [poly(EGDMA-co-HEMA)] base support to obtain different Fe(3+)-containing sorbents and their properties in retention of O-phosphothreonine [Thre(P)] is examined in this paper. Three base supports poly(EGDMA-co-HEMA) (I-III) were obtained using different quantities of initiator in suspension polymerization reactions. These products were submitted to chemical modifications using 1,4-butanediol diglycidyl ether (BDGE) in activation reactions and different chelating agents (iminodiacetic acid, IDA; disodium ethylenediamine tetraacetate, EDTA; and hexamethylenediamine tetrapropanoic acid, HMDTP) in coupling reactions to attain Fe(3+)-containing sorbents. Properties such as specific surface area (S(s)), specific pore volume (V(p)), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), IR spectroscopy, quantity of functional groups (oxirane and carboxyl), amount of chelated metal ion, ligand occupation (L), swelling studies as well as quantity of O-phosphoamino acid retained were used as comparative parameters for matrices. In general, the derivatization reactions proved to be more efficient when higher S(s) of macropores (50-400,000 nm) were available in the matrix. In our case, it was observed when highest percentage of initiator was used. On the other hand, the effect of accessibility of surface area on the yield of coupling reactions was noticed when comparing the different chelating agents since the number of carboxyl groups present in products was higher when the molecular size of the chelating agent was lower. Although all Fe(3+)-containing sorbents resulted efficient to retain Thre(P), the values of retention of the amino acid were slightly higher when IDA-containing matrices were used irrespective of the quantity of metal chelated. This could be probably due to the fact that the IDA ligand could be bounded to the matrix in sites that though accessible for the center of adsorption were hard for Thre(P) to access.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
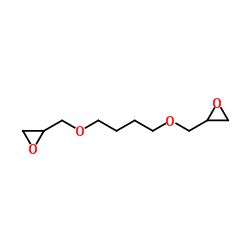 |
UNII:E9μ425FIB
CAS:2425-79-8 |
C10H18O4 |
|
A review of the metabolism of 1,4-butanediol diglycidyl ethe...
2013-12-01 [Dermatol. Surg. 39(12) , 1758-66, (2013)] |
|
An attempt to improve diagnostics of contact allergy due to ...
2004-01-01 [Contact Dermatitis 51(5-6) , 263-72, (2004)] |
|
Chemical mutagenesis testing in Drosophila. IX. Results of 5...
1994-01-01 [Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 23(1) , 51-63, (1994)] |
|
1,4-Butanediol diglycidyl ether (BDE)-crosslinked PEI-g-imid...
2011-06-01 [Mol. Biosyst. 7(6) , 2055-65, (2011)] |
|
Effects of different crosslinking conditions on the chemical...
2013-01-01 [J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 24(1) , 17-35, (2013)] |