Lignocaine plasma levels following topical gel application in laparoscopic and hysteroscopic procedures.
E A Hewitt, G Armstrong, N Beg, S Katz, T G Vancaillie
Index: Anaesth. Intensive Care 40(2) , 292-6, (2012)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The study aim was to determine plasma lignocaine concentrations resulting from topical application of a newly formulated, sterile two-pack lignocaine gel in laparoscopic and hysteroscopic procedures. This was an open label single-centre study in which six female patients underwent laparoscopy and six underwent hysteroscopy. One venous blood sample was extracted pre-gel application, followed by 10 samples over a 24 hour period following application. Samples were centrifuged, stored at -20°C and subsequently analysed for lignocaine and its metabolite, monoethyl-glycinexylidide. Application of gel in doses between 2.7 and 5.8 mg/kg of lignocaine resulted in a maximum plasma concentration in any patient of 1520 ng/ml lignocaine and 240 ng/ml monoethyl-glycinexylidide. These maximum concentrations were recorded in a patient undergoing a laparoscopic procedure and patients undergoing hysteroscopic procedures all recorded lower maximum concentrations compared with patients undergoing laparoscopy; the maximum observed concentrations in a patient having a hysteroscopy were 420 ng/ml lignocaine and 56 ng/ml of monoethyl-glycinexylidide.A new sterile two-pack topical lignocaine gel, applied at the end of laparoscopic and hysteroscopic procedures in doses up to 5.84 mg/kg, resulted in plasma lignocaine levels below those known to have the potential to cause central nervous system toxicity.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
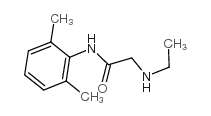 |
Monoethylglycinexylidide
CAS:7728-40-7 |
C12H18N2O |
|
Transplacental Distribution of Lidocaine and Its Metabolite ...
2015-07-01 [Reprod. Sci. 22 , 791-7, (2015)] |
|
Concentrations of dimethylaniline and other metabolites in m...
2015-01-01 [Food Addit. Contam. Part A. Chem. Anal. Control. Expo. Risk Assess. 32 , 1256-64, (2015)] |
|
MEGX test in hepatology: the long-sought ultimate quantitati...
1993-08-01 [J. Hepatol. 19(1) , 4-7, (1993)] |
|
Pharmacokinetics of lidocaine and its metabolite in peridura...
2008-12-01 [Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 64(12) , 1189-96, (2008)] |
|
Effect of 4% topical lidocaine applied to the face on the se...
2010-01-01 [Aesthet. Surg. J. 30(6) , 853-8, (2010)] |