| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
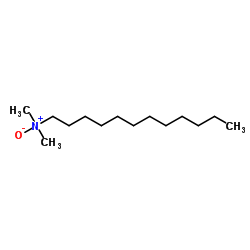 |
N-Dodecyl-N,N-dimethylamine oxide
CAS:1643-20-5 |
|
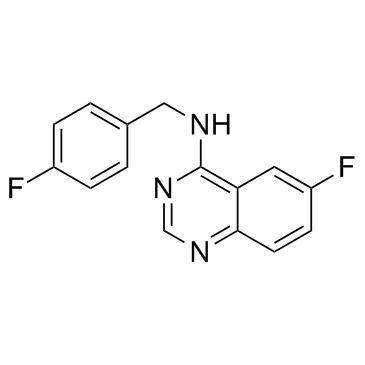 |
Spautin-1
CAS:1262888-28-7 |
|
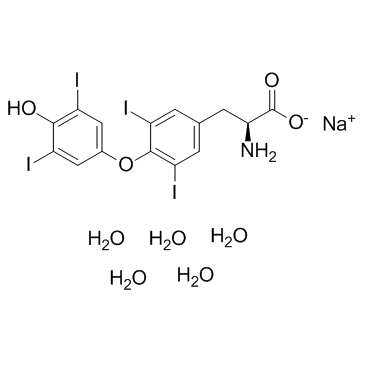 |
Sodium levothyroxine pentahydrate
CAS:6106-07-6 |
|
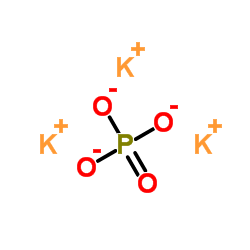 |
Potassium phosphate
CAS:7778-53-2 |
|
 |
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
CAS:60-00-4 |