f-[18F]fluoroethanol and 3-[18F]fluoropropanol: facile preparation, biodistribution in mice, and their application as nucleophiles in the synthesis of [18F]fluoroalkyl aryl ester and ether PET tracers.
Jinhe Pan, Maral Pourghiasian, Navjit Hundal, Joseph Lau, François Bénard, Shoukat Dedhar, Kuo-Shyan Lin
Index: Nucl. Med. Biol. 40(6) , 850-7, (2013)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
2-[(18)F]Fluoroethoxy and 3-[(18)F]fluoropropoxy groups are common moieties in the structures of radiotracers used with positron emission tomography. The objectives of this study were (1) to develop an efficient one-step method for the preparation of 2-[(18)F]fluoroethanol (2-[(18)F]FEtOH) and 3-[(18)F]fluoropropanol (3-[(18)F]FPrOH); (2) to demonstrate the feasibility of using 2-[(18)F]FEtOH as a nucleophile for the synthesis of 2-[(18)F]fluoroethyl aryl esters and ethers; and (3) to determine the biodistribution profiles of 2-[(18)F]FEtOH and 3-[(18)F]FPrOH in mice.2-[(18)F]FEtOH and 3-[(18)F]FPrOH were prepared by reacting n-Bu4N[(18)F]F with ethylene carbonate and 1,3-dioxan-2-one, respectively, in diethylene glycol at 165°C and purified by distillation. 2-[(18)F]fluoroethyl 4-fluorobenzoate and 1-(2-[(18)F]fluoroethoxy)-4-nitrobenzene were prepared by coupling 2-[(18)F]FEtOH with 4-fluorobenzoyl chloride and 1-fluoro-4-nitrobenzene, respectively. Biodistribution and PET/CT imaging studies of 2-[(18)F]FEtOH and 3-[(18)F]FPrOH were performed in normal female Balb/C mice.The preparation of 2-[(18)F]FEtOH and 3-[(18)F]FPrOH took 60 min, and their decay-corrected yields were 88.6 ± 2.0% (n = 9) and 65.6 ± 10.2% (n = 5), respectively. The decay-corrected yields for the preparation of 2-[(18)F]fluoroethyl 4-fluorobenzoate and 1-(2-[(18)F]fluoroethoxy)-4-nitrobenzene were 36.1 ± 5.4% (n = 3) and 27.7 ± 10.7% (n = 3), respectively. Imaging/biodistribution studies in mice using 2-[(18)F]FEtOH showed high initial radioactivity accumulation in all major organs followed by very slow clearance. On the contrary, by using 3-[(18)F]FPrOH, radioactivity accumulated in all major organs was cleared rapidly, but massive in vivo defluorination (31.3 ± 9.57%ID/g in bone at 1h post-injection) was observed.Using 2-[(18)F]FEtOH/3-[(18)F]FPrOH as a nucleophile is a competitive new strategy for the synthesis of 2-[(18)F]fluoroethyl/3-[(18)F]fluoropropyl aryl esters and ethers. Our biodistribution data emphasize the importance of in vivo stability of PET tracers containing a 2-[(18)F]fluoroethyl or 3-[(18)F]fluoropropyl group due to high background and high bone uptake resulting from 2-[(18)F]FEtOH and 3-[(18)F]FPrOH, respectively. This is especially important for their aryl ester derivatives which are prone to in vivo hydrolysis.Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
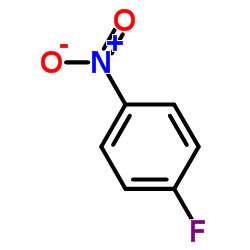 |
1-Fluoro-4-nitrobenzene
CAS:350-46-9 |
C6H4FNO2 |
|
A kinetic-isotope-effect study of catalysis by Vibrio choler...
1993-09-15 [Biochem. J. 294 ( Pt 3) , 653-6, (1993)] |
|
A fluorescent probe for the detection of myeloperoxidase act...
2007-11-01 [Chem. Biol. 14(11) , 1221-31, (2007)] |
|
Effect of reactivity of organics-modified montmorillonite on...
[Chem. Mater. 13(1) , 222-226., (2001)] |
|
A convenient method for N-1 arylation of uracil derivatives....
[Tetrahedron Lett. 47(27) , 4653-57, (2006)] |