Involvement of calmodulin and protein kinase C in cholecystokinin release by bombesin from STC-1 cells.
A Takahashi, S Tanaka, Y Miwa, H Yoshida, A Ikegami, J Niikawa, K Mitamura
Index: Pancreas 21(3) , 231-9, (2000)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The mouse intestinal neuroendocrine tumor cell line STC-1 secretes cholecystokinin (CCK) and other hormones. We investigated the role of Ca2+, calmodulin (CaM), and protein kinase C (PKC) in the regulation of CCK release from STC-1 cells. Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (TPA) significantly stimulated CCK release. Staurosporine significantly inhibited CCK release from STC-1 cells stimulated by TPA in a dose-dependent manner. The absence of extracellular calcium completely inhibited CCK release from TPA-stimulated STC-1 cells. Neurotensin did not stimulate CCK release from these cells. W-7, a CaM antagonist, reduced CCK release from STC-1 cells stimulated by bombesin in a dose-dependent manner. These findings suggest that CaM and PKC play an important role in the regulation of CCK release from STC-1 cells stimulated by bombesin.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
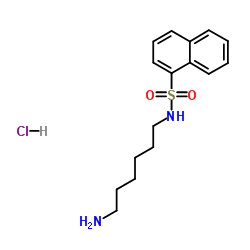 |
W-5 hydrochloride
CAS:61714-25-8 |
C16H23ClN2O2S |
|
Muscarinic receptor-mediated excitation of rat intracardiac ...
2015-08-01 [Neuropharmacology 95 , 395-404, (2015)] |
|
Essential role of Ca2+/calmodulin in Early Endosome Antigen-...
2003-07-01 [Mol. Biol. Cell 14(7) , 2935-45, (2003)] |
|
Occurrence of novel types of nitric oxide synthase in the si...
1995-02-06 [Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 207(1) , 452-9, (1995)] |
|
Regulation of immune complexes binding of macrophages by pec...
1995-02-01 [J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 47(2) , 152-6, (1995)] |
|
Calmodulin-antagonists inhibit vesicular Ca2+ uptake in Dict...
1996-02-01 [Cell Calcium 19(2) , 105-11, (1996)] |