SK2 channels are neuroprotective for ischemia-induced neuronal cell death.
Duane Allen, Shin Nakayama, Masayuki Kuroiwa, Takaaki Nakano, Julie Palmateer, Yasuharu Kosaka, Carmen Ballesteros, Masahiko Watanabe, Chris T Bond, Rafael Luján, James Maylie, John P Adelman, Paco S Herson
Index: J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 31(12) , 2302-12, (2011)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
In mouse hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons, the activity of synaptic small-conductance Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channels type 2 (SK2 channels) provides a negative feedback on N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs), reestablishing Mg(2+) block that reduces Ca(2+) influx. The well-established role of NMDARs in ischemia-induced excitotoxicity led us to test the neuroprotective effect of modulating SK2 channel activity following cerebral ischemia induced by cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CA/CPR). Administration of the SK channel positive modulator, 1-ethyl-benzimidazolinone (1-EBIO), significantly reduced CA1 neuron cell death and improved CA/CPR-induced cognitive outcome. Electrophysiological recordings showed that CA/CPR-induced ischemia caused delayed and sustained reduction of synaptic SK channel activity, and immunoelectron microscopy showed that this is associated with internalization of synaptic SK2 channels, which was prevented by 1-EBIO treatment. These results suggest that increasing SK2 channel activity, or preventing ischemia-induced loss of synaptic SK2 channels, are promising and novel approaches to neuroprotection following cerebral ischemia.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
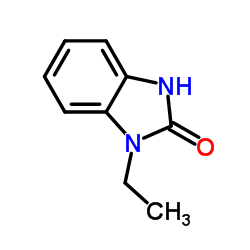 |
1-Ethyl-1,3-dihydro-2H-benzimidazol-2-one
CAS:10045-45-1 |
C9H10N2O |
|
Differentiation between human ClC-2 and CFTR Cl- channels wi...
2014-09-01 [Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 307(5) , C479-92, (2014)] |
|
Type 2 diabetes: increased expression and contribution of IK...
2014-10-15 [Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 307(8) , H1093-102, (2014)] |
|
Firing pattern modulation through SK channel current increas...
2015-02-01 [Mol. Neurobiol. 51(1) , 424-36, (2015)] |
|
Increased Basolateral Amygdala Pyramidal Cell Excitability M...
2015-07-01 [J. Neurosci. 35 , 9730-40, (2015)] |
|
Identification of the functional binding pocket for compound...
2012-01-01 [Nat. Commun. 3 , 1021, (2012)] |